7 Essential Health Benefits & Nutritional Insights

Nutritional Planning for a Balanced Plant-Based Lifestyle
Every cell, tissue, and organ in the human body relies on nutrients for energy to perform its function properly. Nutrients come from the food you eat. A Plant Based Diet with lean meats, poultry, and fish along with lots of vegetables, legumes, fruits, and healthy nuts has numerous health benefits such as reducing chronic disease risk and supporting gut health. Plant Based Diet means you’re consistently eating foods that properly fuel your body for top performance.
Lower Chronic Disease Risk
Plant based diet can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer and obesity. By eating a diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, seeds, lean proteins, and healthy fats we can ensure that our bodies are getting the essential nutrients which gives you health benefits to stay healthy and fight off disease.
Better Blood Sugar Control & Metabolic Health
High quality plant-based diets, characterised by high consumption of fruits, vegetables, nuts, legumes, wholegrains, tea and coffee, are beneficial for T2DM. Plant-based diets are naturally low in saturated fats and high in fiber and antioxidants—optimal for preventing and managing type 2 diabetes.
Vegan diets may provide stronger improvements in certain metabolic parameters due to the complete elimination of animal products. vegan diets tend to result in larger decreases in body weight and fasting glucose levels due to their lower energy density and higher fiber content. Potential for both dietary approaches to improve metabolic outcomes, while suggesting that stricter plant-based diets may offer greater health benefits in blood sugar control.
Weight Management & Satiety
High-fiber, plant-based meals satisfy hunger more effectively. Plant-based diets are naturally lower in caloric density, meaning you can consume larger portions of plant foods while taking in fewer calories. Vegetables, fruits, and legumes are packed with fibre, which promotes satiety, reducing the likelihood of overeating. Plant-based diets are naturally lower in caloric density, meaning you can consume larger portions of plant foods while taking in fewer calories. Vegetables, fruits, and legumes are packed with fibre, which promotes satiety, reducing the likelihood of overeating.
Individuals who eat plant-based diets tend to lose weight and maintain a healthier body weight over time. This can be attributed to several factors:
- Fiber Content
- Lower Saturated Fat
- Balanced Macronutrients
- Improved Metabolism
Whether you’re aiming to fully embrace a plant-based lifestyle or simply add more plant-centric meals to your routine, the benefits for weight management and overall health are substantial. A plant-based diet isn’t merely a short-term weight loss strategy; it’s a sustainable approach that can lead to lasting improvements in your well-being.
By focusing on whole, nutrient-dense plant foods, you can support your body’s health and achieve your weight management goals in a sustainable manner.
Anti-Inflammatory & Antioxidant Boost
A plant-based diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods like fruits and vegetables can effectively reduce inflammation and boost antioxidant intake.
Dietary antioxidants are compounds found in whole foods, that neutralize free radicals, the unstable molecules produced during metabolism, environmental exposure, and other processes. When these free radicals accumulate, they can damage cells, proteins, lipids, and DNA, contributing to oxidative stress, inflammation, and a greater risk of chronic conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, neurodegenerative disorders, and cancer.
Minimizing anti-inflammatory eating pattern means that promote free radical production, like ultra-processed items, refined carbs, and excessive alcohol.
Anti-inflammatory foods
An anti-inflammatory diet should include these foods:
- tomatoes
- olive oil
- green leafy vegetables, such as spinach, kale, and collards
- nuts like almonds and walnuts
- fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, tuna, and sardines
- fruits such as strawberries, blueberries, cherries, and oranges
Gut Microbiome Diversity & Digestive Health
A biome is a distinct ecosystem characterized by its environment and its inhabitants. Your gut — inside your intestines — is in fact a miniature biome, populated by trillions of microscopic organisms. These microorganisms include over a thousand species of bacteria, as well as viruses, fungi and parasites.
Think of your gut microbiome as a vibrant native garden that nourishes and heals you. When the ‘soil’ of this internal garden is rich and well-tended, you flourish alongside it. But if that soil becomes depleted, polluted, or choked with weeds and pests, the entire ecosystem—and your health—can suffer.
Gut bacteria play a vital role in maintaining your health:
- They ferment complex carbohydrates and dietary fibers you can’t digest, producing short‑chain fatty acids (SCFAs)—valuable nutrients that support your gut lining, metabolism, and immune system
- These microbes also provide enzymes that enable the synthesis of essential vitamins such as B₁ (thiamine), B₉ (folate), B₁₂ and K.
In essence, your gut flora breaks down indigestible fibers into SCFAs and helps produce vital vitamins—functions crucial for your digestion, nutrient absorption, and overall wellness.
Enhanced Cognitive Health & Longevity
Characteristics of Plant based diets such as protein restriction and restriction of certain amino acids are known to extend the life span. While there is ample evidence from animal studies, large-scale human studies, which also provide insight into the specific mechanisms of the effect of Plant based diets on longevity, are missing. However, due to the lower protein content, there appears to be an age limit for the anticipated health benefits, as adults over 65 require larger amounts of protein.
Tips for Nutritional Planning & Implementation
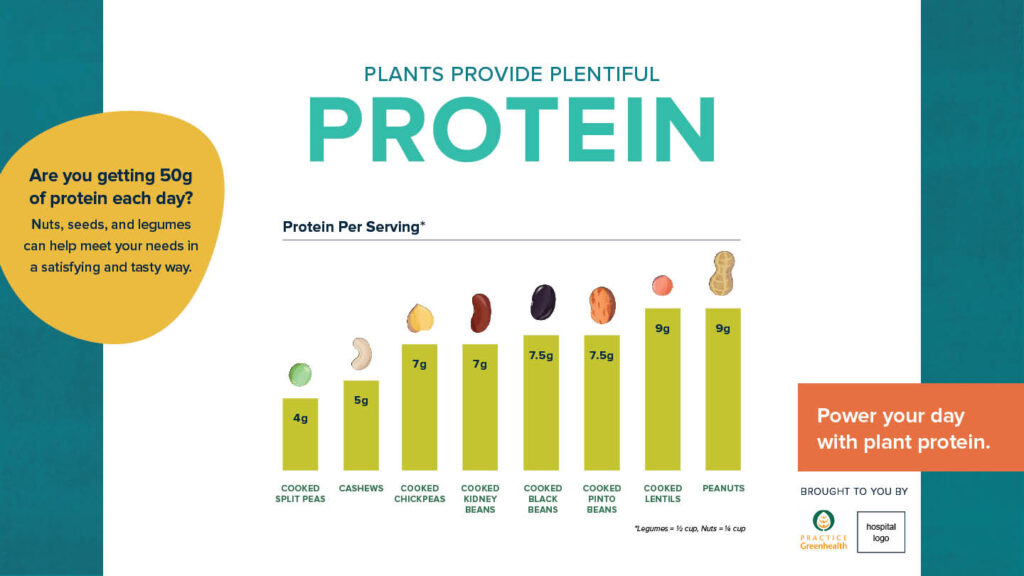
- Plan : Set Goals, see on your eating habits, Prepare a meal plan, also see on cooking methods.
- Build nutritious diet : Decide weekly intake, Focus on unprocessed foods, Focus on Proteins, drink good amount of water.
- Make it Sustainable : make small changes, include plant based foods that you can enjoy, include physical activity.
- Specific Tips : Read Nutrition labels, use online resources, Choose healthy options, Plan ahead with meal preparation.
“You’ll nourish your body, safeguard your mind, and support our planet—all with every delicious plant-based bite you take!”
