What is Physical Health? | What is the Key-Pillars of Health? | Healthy Outside, Happy Inside: Unlocking Physical Wellness
What is physical health?
Fitness and Health Enthusiast: Manthan Dutta; Physical health refers to the optimal functioning of the body’s systems — from the way your muscles and organs perform to how effectively your body repairs itself and responds to daily challenges. It is one of the core dimensions of overall well-being and directly impacts how we feel, move, grow, and live each day.
Good physical health means more than just the absence of illness. It involves maintaining strength, flexibility, endurance, and balance, as well as nurturing the body through proper care and conscious choices. This includes regular movement, nutritious food, restorative sleep, and preventive care. The way we treat our bodies — from the foods we eat and the habits we form to how we manage stress — determines how well it can support us in everything we do.

What is Physical Health? | What is the Key-Pillars of Health? | Healthy Outside, Happy Inside: Unlocking Physical Wellness
In essence, physical health is the foundation upon which our mental clarity, emotional stability, and overall quality of life are built. When we prioritize it, we empower ourselves to live more energetically, confidently, and fully. Physical health can be defined as the normal functioning of the body. Representing one dimension of total well-being, it’s about how your body grows, feels and moves, how you care for it, and what you put into it.
Pillars of Physical Health
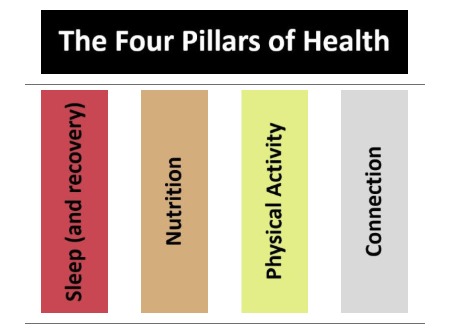
The four pillars of health are Sleep (and recovery), Nutrition, Physical Activity and Connection.
Sleep

Sleep is often one of the most underestimated yet powerful tools for improving overall health, performance, and mental well-being. In our fast-paced lifestyles, it’s common to sacrifice sleep in favor of work, entertainment, or productivity — but this can come at a significant cost.
Getting adequate and restful sleep is essential for maintaining a healthy body and mind. Quality sleep plays a critical role in regulating metabolism, supporting immune function, balancing hormones, and facilitating cellular repair. It helps prevent a range of serious health issues such as excess weight gain, cardiovascular disease, weakened immunity, and increased risk of chronic illnesses like diabetes and hypertension.
It’s not just the number of hours you sleep that matters — the quality of your sleep is equally important. Deep, uninterrupted sleep cycles are what allow your body to truly rest, recover, and recharge. Therefore, establishing and maintaining consistent sleep patterns, avoiding screen time before bed, creating a calming night time routine, and ensuring a comfortable sleep environment can greatly improve your sleep hygiene.
Nutrition

Proper and balanced nutrition plays a crucial role in enhancing physical performance, supporting faster recovery, boosting mental clarity, and stabilizing overall mood. It’s not just about eating enough — it’s about eating right. This means consuming meals that provide the right proportion of macronutrients — proteins, carbohydrates, and healthy fats — tailored to your body’s needs and activity level.
In addition to macronutrients, a well-rounded diet must include essential vitamins, minerals, and micronutrients that support critical bodily functions such as immunity, muscle repair, hormone balance, and brain function. A consistent intake of nutrient-dense foods can help reduce fatigue, prevent injuries, improve focus, and maintain emotional balance.
Physical Activity
The human body is inherently designed for movement — it thrives on physical activity. When we lead a sedentary lifestyle and neglect regular exercise, our bodies begin to suffer in multiple ways. One of the first noticeable effects is a reduction in joint mobility and flexibility, which can lead to stiffness, discomfort, and even chronic pain. Over time, the lack of movement can cause muscular imbalances and dysfunctions that affect posture and coordination.
Beyond physical discomfort, inactivity takes a toll on overall health, contributing to a decline in mental, physical, and physiological well-being. Prolonged sedentary behavior is closely linked to a range of serious health conditions, including weight gain, Type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain forms of cancer. It can also negatively impact mental health, leading to mood disorders such as anxiety and depression, largely due to reduced circulation, hormonal imbalance, and lack of endorphin release.
Connection
Connection refers to the quality of our relationships and sense of belonging — with others, with ourselves, and with the world around us. Human beings are social by nature, and having strong, positive connections is essential for both mental and physical health.
This pillar includes:

- 💬 Meaningful relationships with family, friends, partners, and community
- 🤝 Social support during stress, illness, or emotional struggles
- 🧘 Connection to self, through practices like mindfulness, self-awareness, and self-compassion
- 🌍 Spiritual or environmental connection, for those who find meaning in nature, purpose, or faith
A lack of connection — often seen as loneliness or isolation — has been linked to increased stress levels, anxiety, depression, weakened immunity, and even higher risks of chronic diseases.
Conclusion
Physical health is the foundation of overall well-being, deeply intertwined with how we sleep, eat, move, and connect. By nurturing these four pillars — Sleep, Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Connection — we not only enhance our physical strength and stamina but also improve our emotional resilience and quality of life. A healthy body supports a healthy mind, and together, they enable us to live with energy, purpose, and balance. Taking small, consistent steps in each area can lead to profound long-term benefits for both body and soul.

Sourav Saha
very helpful